Abstract
Sinds the end of the 80's, standard rainbow method is used to measure the size and temperature
of individual spray droplets, and has many applications in fuel combustion research.
Nevertheless, major problems (like temperature gradients inside the droplet, non-sphericity
of the droplet,...) affect the temperature measurement.
However, the main source of measurement uncertainty, for standard rainbow thermometry, occurs for
droplets that are non-spherical. Take a look at Figure 1 to have an idea of the problem. It
shows an interaction between the primary and the secondary rainbow formed by non-spherical droplet.
It is clear that the position of the rainbow depends not only on the droplet temperature
but also on its shape. This include an ambiguity in the temperature measurement.
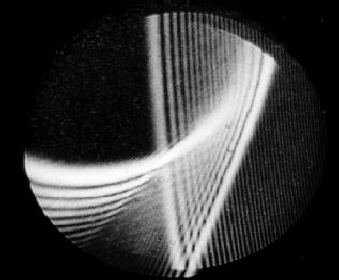 Fig. 1
A typical rainbow pattern formed by a non-spherical droplet.
Fig. 1
A typical rainbow pattern formed by a non-spherical droplet.
Global rainbow thermometry primarily aims at illuminating the non-sphericity effects that
exists for the standard rainbow technique since its invention in 1988.
Figure 2 shows a picture of the setup. A CW Argon-ion laser beam illuminates a
water spray. The most important remark is that there is no spatial filter like for
standard rainbow thermometry. Instead, a transparent piece of paper is installed
at the position of the focal plane of the receiving lens. This means that not one
but all the droplets crossing the laser beam will contribute to the angular scattered
ligth distribution, visible on the transparent screen. This results in the so-called
global rainbow pattern that is recorded from the other side of the transparent screen
by a digital camera.
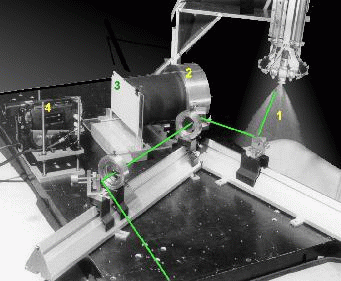 Fig. 2
Picture of the setup. One distinguishes the water spray (1), receiving lens (2),
transparent screen (3) and video camera (4). The laser beam is added during
post-processing of the photograph and does not represent the real thickness.
Fig. 2
Picture of the setup. One distinguishes the water spray (1), receiving lens (2),
transparent screen (3) and video camera (4). The laser beam is added during
post-processing of the photograph and does not represent the real thickness.
A typical global rainbow pattern is seen in Figure 3.
It is recorded when the water works at stable
ambient temperature. Although most probably numerous non-spherical droplets are
crossing the laser beam, the position of the global rainbow pattern is not moving.
This implies that the pattern is formed by constructive interference of the spherical
droplets, because for each of them the geometrical rainbow angle is indentical.
Destructive interference occurs for the non-spherical droplets, because their
interference fringes are randomly oriented and thus yield a uniform background.
Consequently, there is no need for complex selection criteria to look for global
rainbow pattern from spherical droplets. The selection is done automatically, just like
the rainbow in the sky is a static phenomenon, even though numerous raindrops
are not spherical.
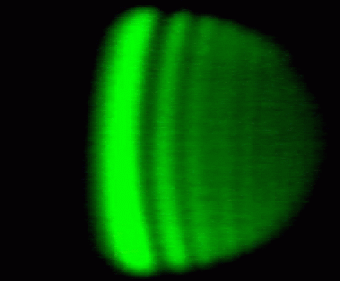 Fig. 3
A typical global rainbow pattern in a water spray recorded by a video camera.
Fig. 3
A typical global rainbow pattern in a water spray recorded by a video camera.